0. 사전세팅
- JDK, Eclipse 설치
- Tomcat, Apache 서버 세팅 (이클립스 프로젝트 구성 시 자동설치 가능)
- 이클립스를 통해 dynamic web project 생성
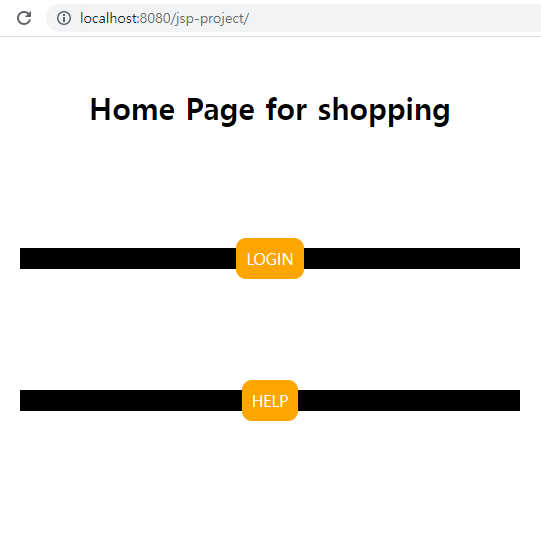
1. index.jsp 생성
서버 index page
초기 프로젝트 생성시 webapp 폴더가 document root
home 컨트롤러(최초 라우팅 기능)로 연결
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>project web application</title>
<link href="static/common.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="title">Home Page for shopping</div><br>
<div class="link"><a href = "/jsp-project/home?action=login">LOGIN</a></div><br>
<div class="link"><a href = "/jsp-project/home?action=help">HELP</a></div>
</body>
</html>
2. controller 패키지 생성
패키지 생성 디렉토리 JavaResources/src/main/java/controller
해당 디렉토리에 생성된 java파일은 src/main/java로 위치
Home controller 생성 및 /home 맵핑
DoLogin controller 생성 및 /doLogin 맵핑
home.java
package controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class Home
*/
@WebServlet("/home")
public class Home extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public Home() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String action = request.getParameter("action");
String page = null;
if(action.equals("login")){
page="/view/loginform.jsp";
}else if(action.equals("help")){
page="/view/help.jsp";
}else {
page="/view/error.jsp";
}
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(page);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
}
3. view 폴더 생성
각 컨트롤러에서 라우팅 되어 데이터를 넘겨받는 template 영역
webapp/view 폴더 생성
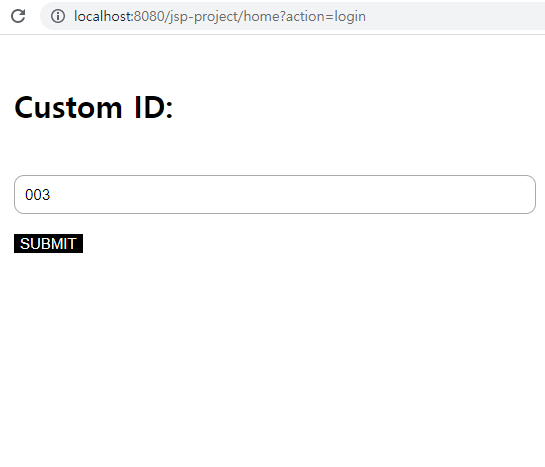
view 폴더 내 error.jsp(에러), help.jsp(HELP 클릭), loginform.jsp (LOGIN 클릭)생성
loginform.jsp 파일은 input 입력값을 DoLogin 컨트롤러로 전달 (key값 “action”)
loginform.java
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=EUC-KR"
pageEncoding="EUC-KR"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="EUC-KR">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<link href="static/common.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<form action="/jsp-project/doLogin" method="get">
<div class="inputTitle">Custom ID:</div>
<input class="input" type = "text" name="customerId"/> <br>
<input class="button" type = "submit" value = "SUBMIT" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
4. model/service 영역 생성
model영역 : DAO, DTO로 구성 (지금은 DB설치 없이 DAO 생략)
service영역 : model 객체 및 데이터 최종 가공
service 영역에서 bean(DTO) 객체 생성시 생성자로 사용자 데이터 임의 생성
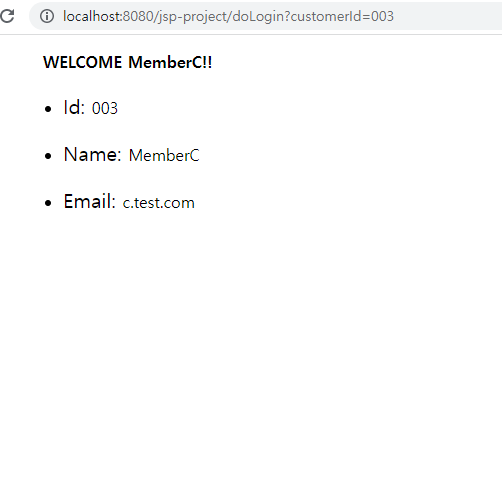
model/Customer.java
package model;
public class Customer {
private String id;
private String name;
private String email;
public Customer(String id, String name, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
service/CustomerService.java
package service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import model.Customer;
public class CustomerService {
private Map<String, Customer> customers;
public CustomerService() {
customers = new HashMap<String, Customer>();
addCustomer(new Customer("001", "MemberA", "a.test.com"));
addCustomer(new Customer("002", "MemberB", "b.test.com"));
addCustomer(new Customer("003", "MemberC", "c.test.com"));
addCustomer(new Customer("004", "MemberD", "d.test.com"));
addCustomer(new Customer("005", "MemberE", "e.test.com"));
addCustomer(new Customer("006", "MemberF", "f.test.com"));
}
public void addCustomer(Customer customer) {
customers.put(customer.getId(), customer);
}
public Customer findCustomer(String id) {
if(id != null) {
return customers.get(id.toLowerCase());
}else {
return null;
}
}
}